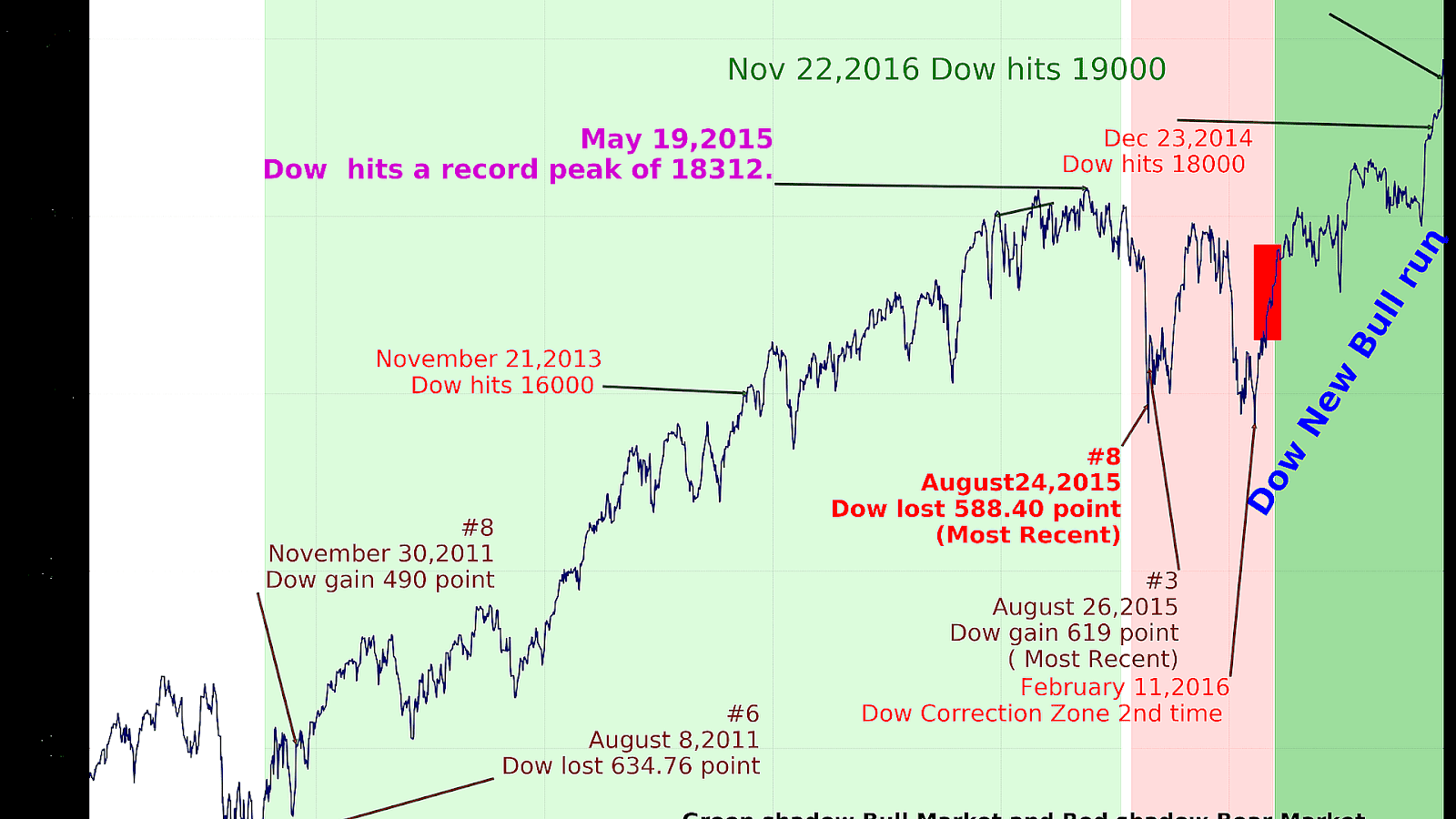
The Dow Jones Average Index is a crucial indicator of the stock market's performance, representing the health of the economy and guiding investors in their decision-making processes. As one of the oldest and most widely recognized stock market indices, it reflects the stock prices of 30 significant publicly traded companies in the United States. This article will delve into the intricacies of the Dow Jones Average Index, providing a thorough understanding of its components, historical significance, and impact on the global economy.
The Dow Jones Average Index, commonly referred to as the Dow, serves as a barometer for the stock market and the economy as a whole. It was created by Charles Dow in 1896 and has since evolved into a key reference for investors, analysts, and economists. In this article, we will explore its structure, how it is calculated, and its relevance in today's financial landscape.
As investors and financial enthusiasts seek to navigate the complexities of the market, understanding the Dow Jones Average Index becomes essential. This guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to make informed investment decisions and better comprehend market trends.
Table of Contents
- What is the Dow Jones Average Index?
- History of the Dow Jones Average Index
- How is the Dow Jones Average Index Calculated?
- Components of the Dow Jones Average Index
- Importance of the Dow Jones Average Index
- Criticism of the Dow Jones Average Index
- Investing in the Dow Jones Average Index
- Future of the Dow Jones Average Index
What is the Dow Jones Average Index?
The Dow Jones Average Index is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 30 significant publicly traded companies in the United States. It is one of the main indicators of stock market performance and is often used to gauge the overall health of the economy. The index is price-weighted, meaning that companies with higher stock prices have a more significant impact on the index's overall value.
Key Features of the Dow Jones Average Index
- Consists of 30 major companies across various sectors.
- Price-weighted index, affecting how changes in stock prices impact the index.
- Regularly updated to reflect changes in the market and economy.
History of the Dow Jones Average Index
The Dow Jones Average Index was first introduced on May 26, 1896, by Charles Dow, co-founder of Dow Jones & Company. It initially included 12 industrial companies, which later expanded to 20 and then to 30. The index has undergone several changes in its composition to adapt to the evolving economic landscape.
Significant Milestones
- 1896: Establishment of the Dow Jones Average Index with 12 companies.
- 1928: Expansion to include 30 companies.
- 1985: The index was adjusted to account for stock splits and changes in company structure.
How is the Dow Jones Average Index Calculated?
The calculation of the Dow Jones Average Index is relatively straightforward. It is determined by summing the prices of all 30 stocks and then dividing that sum by a divisor. The divisor is adjusted to account for stock splits and other factors that could affect the index's value.
Calculation Formula
The formula for calculating the Dow is as follows:
Dow Jones Average = (Sum of stock prices) / Divisor
Components of the Dow Jones Average Index
The Dow Jones Average Index includes 30 large publicly traded companies from various industries, including technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods. Some of the notable companies in the index include:
- Apple Inc.
- Microsoft Corporation
- Johnson & Johnson
- Visa Inc.
- Coca-Cola Company
Sector Representation
The companies in the Dow represent a diverse range of sectors, which allows the index to provide a comprehensive overview of the market's performance. This diversity helps investors gauge trends in different industries and make informed investment decisions.
Importance of the Dow Jones Average Index
The Dow Jones Average Index is widely regarded as a vital tool for investors and analysts. Its importance lies in several key aspects:
- Benchmark for Market Performance: The Dow serves as a benchmark for the overall performance of the stock market.
- Economic Indicator: Changes in the Dow can signal shifts in the economy and investor sentiment.
- Investment Strategy: Many mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are designed to track the performance of the Dow.
Criticism of the Dow Jones Average Index
Despite its significance, the Dow Jones Average Index has faced criticism over the years. Some of the common criticisms include:
- Price-Weighted Nature: The price-weighted calculation can skew the index, giving more influence to higher-priced stocks regardless of their market capitalization.
- Limited Representation: With only 30 companies, some argue that the index does not provide a comprehensive view of the entire market.
Investing in the Dow Jones Average Index
Investing in the Dow can be an effective strategy for those looking to gain exposure to the broader market. Investors can consider various options:
- Index Funds: Mutual funds or ETFs that track the performance of the Dow.
- Individual Stocks: Purchasing shares of the companies included in the Dow.
Future of the Dow Jones Average Index
The future of the Dow Jones Average Index remains optimistic, as it continues to adapt to the changing economic landscape. With advancements in technology and evolving market dynamics, the index is likely to remain a key indicator of market performance.
Conclusion
In summary, the Dow Jones Average Index is a crucial component of the financial landscape, serving as a benchmark for market performance and an indicator of economic health. Understanding its structure, historical significance, and impact can empower investors to navigate the complexities of the stock market effectively. We encourage you to explore investment opportunities related to the Dow and stay informed about its developments.
Call to Action
If you found this article helpful, please leave a comment, share it with your friends, or explore more of our articles for further insights into the world of finance and investing.
Positive Closing
Thank you for reading, and we look forward to welcoming you back for more informative content on financial markets and investment strategies!
Understanding The Concept Of Fold In Web Design: Best Practices And Techniques
Wayfair: The Ultimate Guide To Online Home Goods Shopping
Unveiling Seo Ye Ji: The Rising Star Of South Korean Cinema