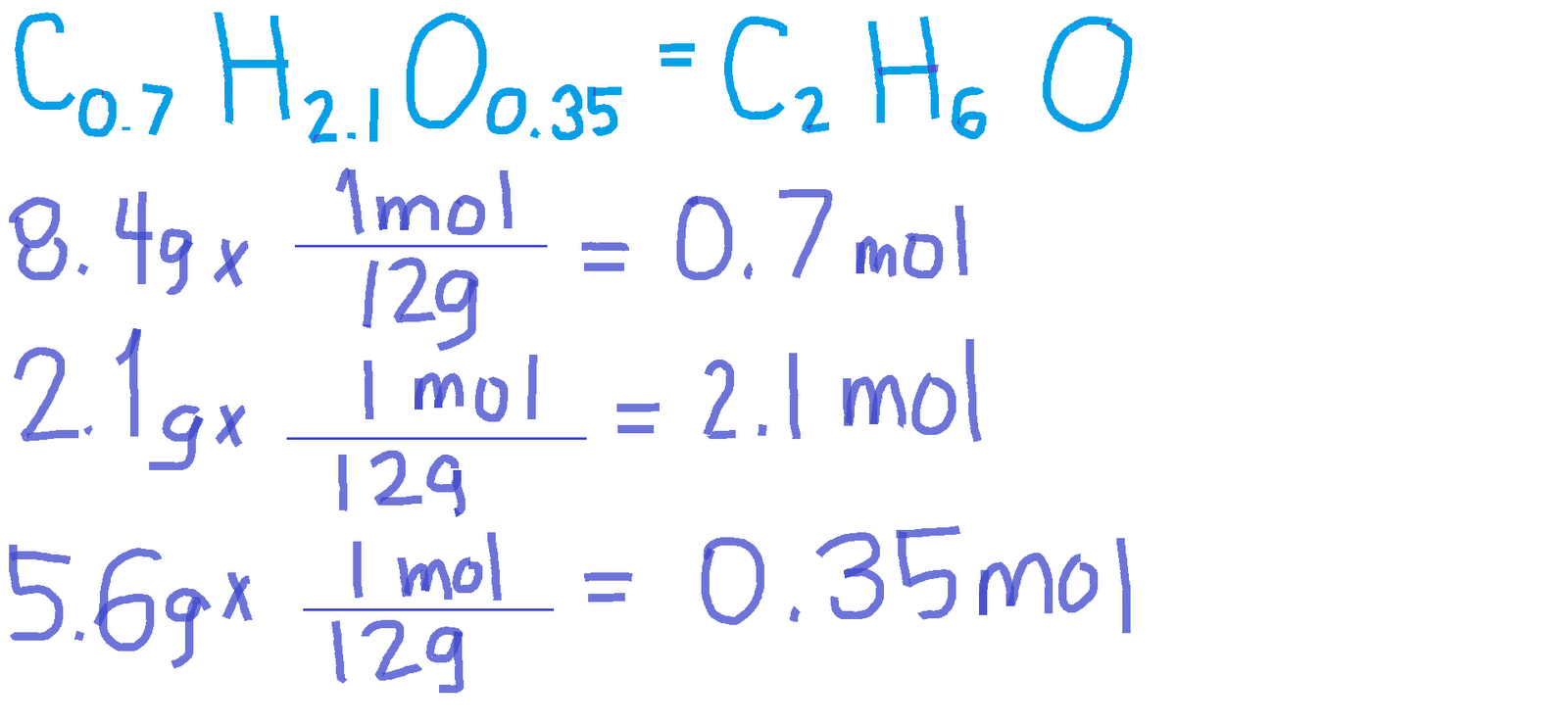The empirical formula is a fundamental concept in chemistry that provides insight into the composition of a compound. It represents the simplest whole-number ratio of elements in a chemical compound. Understanding how to derive and interpret empirical formulas is essential for students, educators, and professionals in the field of chemistry. This article delves into the intricacies of empirical formulas, their importance, and how they differ from molecular formulas.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the definition of empirical formulas, the steps involved in calculating them, and the significance they hold in real-world applications. Whether you are a student preparing for exams or a professional seeking to refresh your knowledge, this article aims to provide valuable insights into this crucial aspect of chemistry.
As we progress through this article, we will cover various sub-topics, including the relationship between empirical and molecular formulas, examples of empirical formulas, and their applications in different scientific fields. By the end of this guide, you will have a clear understanding of empirical formulas and their relevance in both academic and practical contexts.
Table of Contents
- Definition of Empirical Formula
- How to Calculate Empirical Formula
- Step 1: Determine the Mass of Each Element
- Step 2: Convert Mass to Moles
- Step 3: Find the Simplest Ratio
- Examples of Empirical Formulas
- Difference Between Empirical and Molecular Formulas
- Applications of Empirical Formulas
- Common Mistakes in Calculating Empirical Formulas
- Importance of Empirical Formulas in Chemistry
- Conclusion
Definition of Empirical Formula
The empirical formula of a compound is defined as the simplest whole-number ratio of the different types of atoms present in the compound. For example, the empirical formula for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is HO, indicating that the ratio of hydrogen to oxygen is 1:1. This simplified representation is particularly useful in understanding the elemental composition of compounds without delving into their molecular structure.
How to Calculate Empirical Formula
Calculating the empirical formula involves several steps that require careful measurement and analysis of the compound's components. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Determine the Mass of Each Element
Begin by measuring the mass of each element in the compound. This can be done using analytical balances in a laboratory setting. Ensure that the measurements are accurate to obtain a reliable empirical formula.
Step 2: Convert Mass to Moles
Next, convert the mass of each element to moles by dividing the mass by the atomic mass of the element (found on the periodic table). The formula to convert mass to moles is:
- Moles = Mass (g) / Atomic Mass (g/mol)
Step 3: Find the Simplest Ratio
After obtaining the number of moles for each element, divide each mole value by the smallest number of moles calculated. This will yield the simplest whole-number ratio of the elements in the compound, which constitutes the empirical formula.
Examples of Empirical Formulas
Let’s look at some examples of empirical formulas to solidify your understanding:
- For glucose (C6H12O6), the empirical formula is CH2O.
- For benzene (C6H6), the empirical formula is CH.
- For ammonium sulfate ((NH4)2SO4), the empirical formula is (NH4)SO4.
Difference Between Empirical and Molecular Formulas
It’s crucial to distinguish between empirical and molecular formulas. While the empirical formula provides the simplest ratio of elements, the molecular formula specifies the actual number of each type of atom in a molecule of the compound. For instance, the molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6, whereas its empirical formula is CH2O. Understanding this difference is vital for accurate chemical analysis.
Applications of Empirical Formulas
Empirical formulas have numerous applications across various fields of science:
- In organic chemistry, empirical formulas help in identifying compounds and understanding their properties.
- In pharmacology, they assist in drug formulation by determining the ratio of active ingredients.
- In environmental science, empirical formulas are used to analyze pollutants and their concentrations in ecosystems.
Common Mistakes in Calculating Empirical Formulas
When calculating empirical formulas, students often make several common mistakes, including:
- Failing to convert grams to moles correctly.
- Not simplifying the ratios to the smallest whole numbers.
- Misinterpreting the chemical composition of compounds.
Importance of Empirical Formulas in Chemistry
Empirical formulas play a crucial role in various chemical processes and analyses. They provide a foundation for understanding chemical reactions, stoichiometry, and molecular behavior. By grasping the concept of empirical formulas, chemists can make informed predictions about the properties and reactivity of substances.
Conclusion
In summary, the empirical formula is a vital concept in chemistry that conveys essential information about the composition of compounds. By following the outlined steps to calculate empirical formulas, you can gain a deeper understanding of how elements interact and form various substances. We encourage you to apply this knowledge in practical scenarios and share your insights in the comments below. For more articles on chemistry and related topics, feel free to explore our website.
Thank you for reading! We hope you found this article informative and engaging. Don’t hesitate to return for more expert insights into the fascinating world of chemistry.
Detroit Lions Vs 49ers: A Deep Dive Into The Rivalry
Washington Vs Texas Game: A Detailed Overview Of The Rivalry
Tortilla Blanket: The Ultimate Cozy Experience For All Ages